Humans are naturally capable of learning throughout their lives without forgetting what they already know. They can also infer and comprehend new concepts from just a few, or even no examples. However, deep neural networks lack such abilities, and typically require large-scale, static datasets.
Many real-world applications involve data that is dynamically evolving, but sparse in nature. For instance, patient data is continuously generated, but it may be limited in cases of rare diseases and difficult to share due to privacy concerns. Motivated by this, I aim to build practical models that can reason and learn more like humans: learn incrementally, generalize from restricted data, and remain stable under distribution shifts.
2026
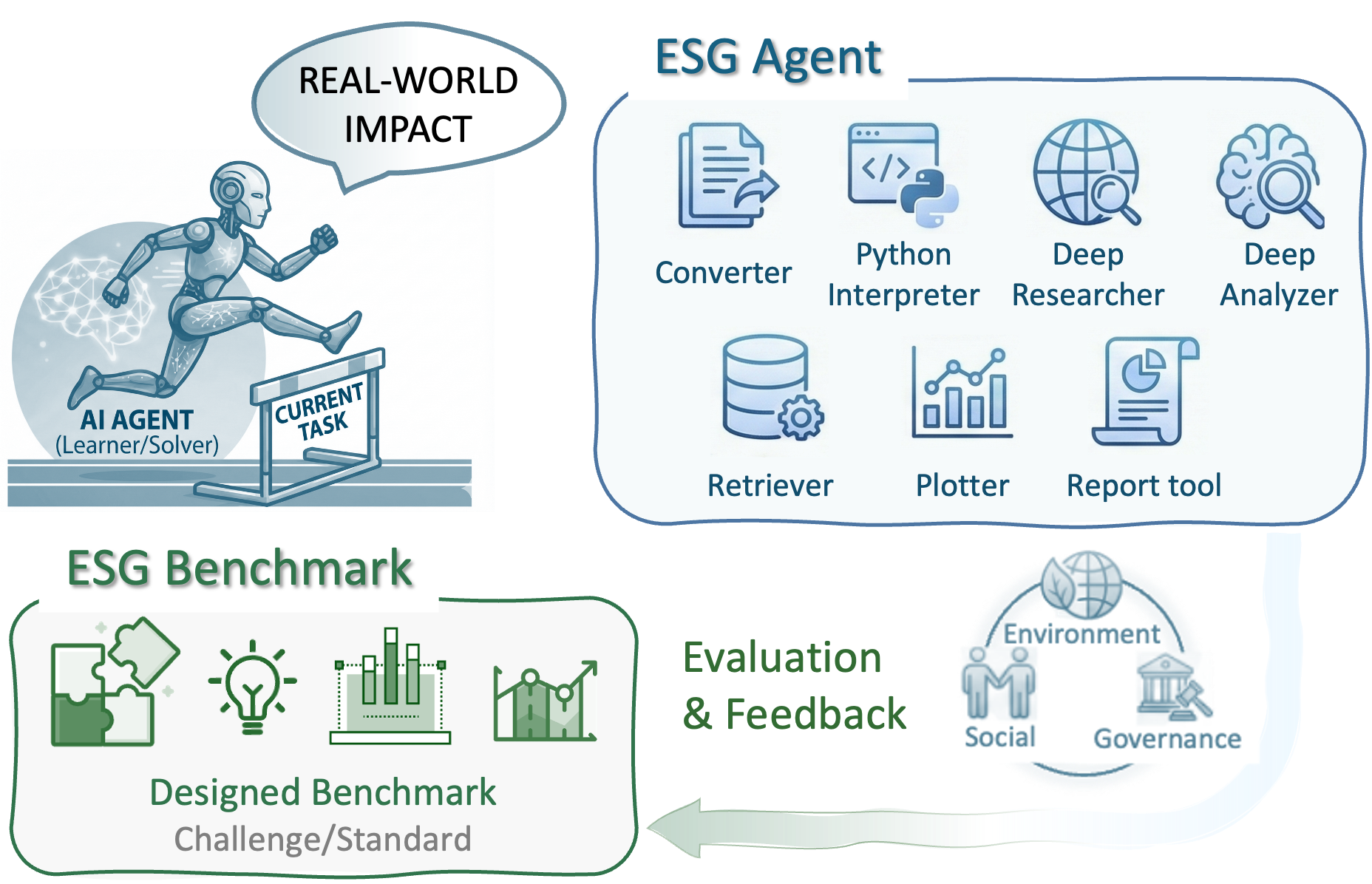
Advancing ESG Intelligence: An Expert-level Agent and Comprehensive Benchmark for Sustainable Finance
Yilei Zhao, Wentao Zhang, Lei Xiao, Yandan Zheng, Mengpu Liu, Wei Yang Bryan Lim
Under review.
Environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria are essential for evaluating corporate sustainability and ethical performance. However, professional ESG analysis is hindered by data fragmentation across unstructured sources, and existing large language models (LLMs) often struggle with the complex, multi-step workflows required for rigorous auditing. To address these limitations, we introduce ESGAgent, a hierarchical multi-agent system empowered by a specialized toolset, including retrieval augmentation, web search and domain-specific functions, to generate in-depth ESG analysis. Complementing this agentic system, we present a comprehensive three-level benchmark derived from 310 corporate sustainability reports, designed to evaluate capabilities ranging from atomic common-sense questions to the generation of integrated, in-depth analysis. Empirical evaluations demonstrate that ESGAgent outperforms state-of-the-art closed-source LLMs with an average accuracy of 84.15% on atomic question-answering tasks, and excels in professional report generation by integrating rich charts and verifiable references. These findings confirm the diagnostic value of our benchmark, establishing it as a vital testbed for assessing general and advanced agentic capabilities in high-stakes vertical domains.
# AI4Finance # benchmark and datasets # ESG Finance
Advancing ESG Intelligence: An Expert-level Agent and Comprehensive Benchmark for Sustainable Finance
Yilei Zhao, Wentao Zhang, Lei Xiao, Yandan Zheng, Mengpu Liu, Wei Yang Bryan Lim
Under review.
Environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria are essential for evaluating corporate sustainability and ethical performance. However, professional ESG analysis is hindered by data fragmentation across unstructured sources, and existing large language models (LLMs) often struggle with the complex, multi-step workflows required for rigorous auditing. To address these limitations, we introduce ESGAgent, a hierarchical multi-agent system empowered by a specialized toolset, including retrieval augmentation, web search and domain-specific functions, to generate in-depth ESG analysis. Complementing this agentic system, we present a comprehensive three-level benchmark derived from 310 corporate sustainability reports, designed to evaluate capabilities ranging from atomic common-sense questions to the generation of integrated, in-depth analysis. Empirical evaluations demonstrate that ESGAgent outperforms state-of-the-art closed-source LLMs with an average accuracy of 84.15% on atomic question-answering tasks, and excels in professional report generation by integrating rich charts and verifiable references. These findings confirm the diagnostic value of our benchmark, establishing it as a vital testbed for assessing general and advanced agentic capabilities in high-stakes vertical domains.
2025
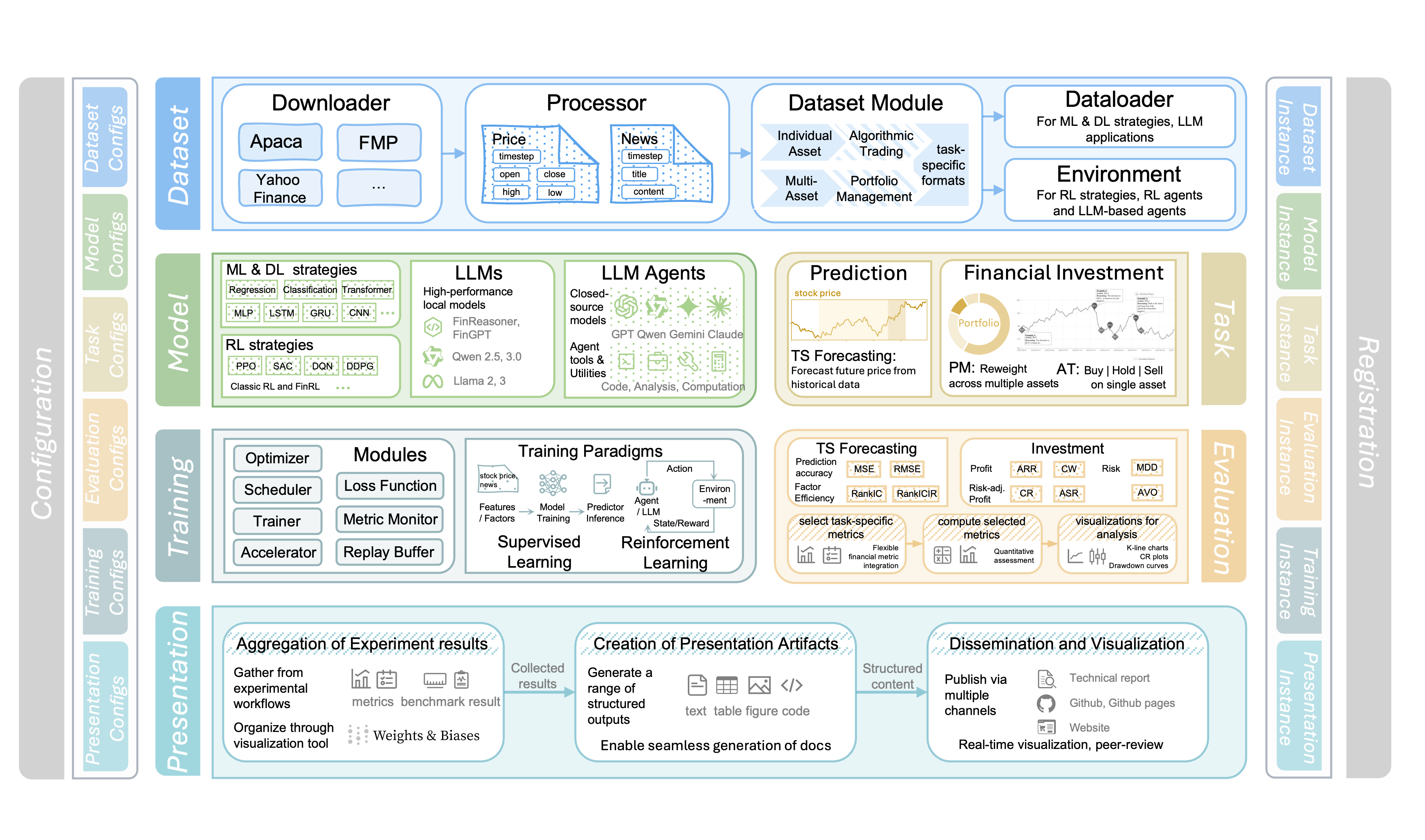
FinWorld: An All-in-One Open-Source Platform for End-to-End Financial AI Research and Deployment
Wentao Zhang*, Yilei Zhao*, Chuqiao Zong, Xinrun Wang†, Bo An
Proceedings of SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining (KDD), 2026
[TL;DR] [Paper] [Code] [Website]
Financial AI holds great promise for transforming modern finance, with the potential to support a wide range of tasks such as market forecasting, portfolio management, quantitative trading, and automated analysis. However, existing platforms remain limited in task coverage, lack robust multimodal data integration, and offer insufficient support for the training and deployment of large language models (LLMs). In response to these limitations, we present FinWorld, an all-in-one open-source platform that provides end-to-end support for the entire financial AI workflow, from data acquisition to experimentation and deployment. FinWorld distinguishes itself through native integration of heterogeneous financial data, unified support for diverse AI paradigms, and advanced agent automation, enabling seamless development and deployment. Leveraging data from 2 representative markets, 4 stock pools, and over 800 million financial data points, we conduct comprehensive experiments on 4 key financial AI tasks. These experiments systematically evaluate deep learning and reinforcement learning algorithms, with particular emphasis on RL-based finetuning for LLMs and LLM Agents. The empirical results demonstrate that FinWorld significantly enhances reproducibility, supports transparent benchmarking, and streamlines deployment, thereby providing a strong foundation for future research and real-world applications.
# AI4Finance # portfolio management # quantitative trading
FinWorld: An All-in-One Open-Source Platform for End-to-End Financial AI Research and Deployment
Wentao Zhang*, Yilei Zhao*, Chuqiao Zong, Xinrun Wang†, Bo An
Proceedings of SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining (KDD), 2026
Financial AI holds great promise for transforming modern finance, with the potential to support a wide range of tasks such as market forecasting, portfolio management, quantitative trading, and automated analysis. However, existing platforms remain limited in task coverage, lack robust multimodal data integration, and offer insufficient support for the training and deployment of large language models (LLMs). In response to these limitations, we present FinWorld, an all-in-one open-source platform that provides end-to-end support for the entire financial AI workflow, from data acquisition to experimentation and deployment. FinWorld distinguishes itself through native integration of heterogeneous financial data, unified support for diverse AI paradigms, and advanced agent automation, enabling seamless development and deployment. Leveraging data from 2 representative markets, 4 stock pools, and over 800 million financial data points, we conduct comprehensive experiments on 4 key financial AI tasks. These experiments systematically evaluate deep learning and reinforcement learning algorithms, with particular emphasis on RL-based finetuning for LLMs and LLM Agents. The empirical results demonstrate that FinWorld significantly enhances reproducibility, supports transparent benchmarking, and streamlines deployment, thereby providing a strong foundation for future research and real-world applications.
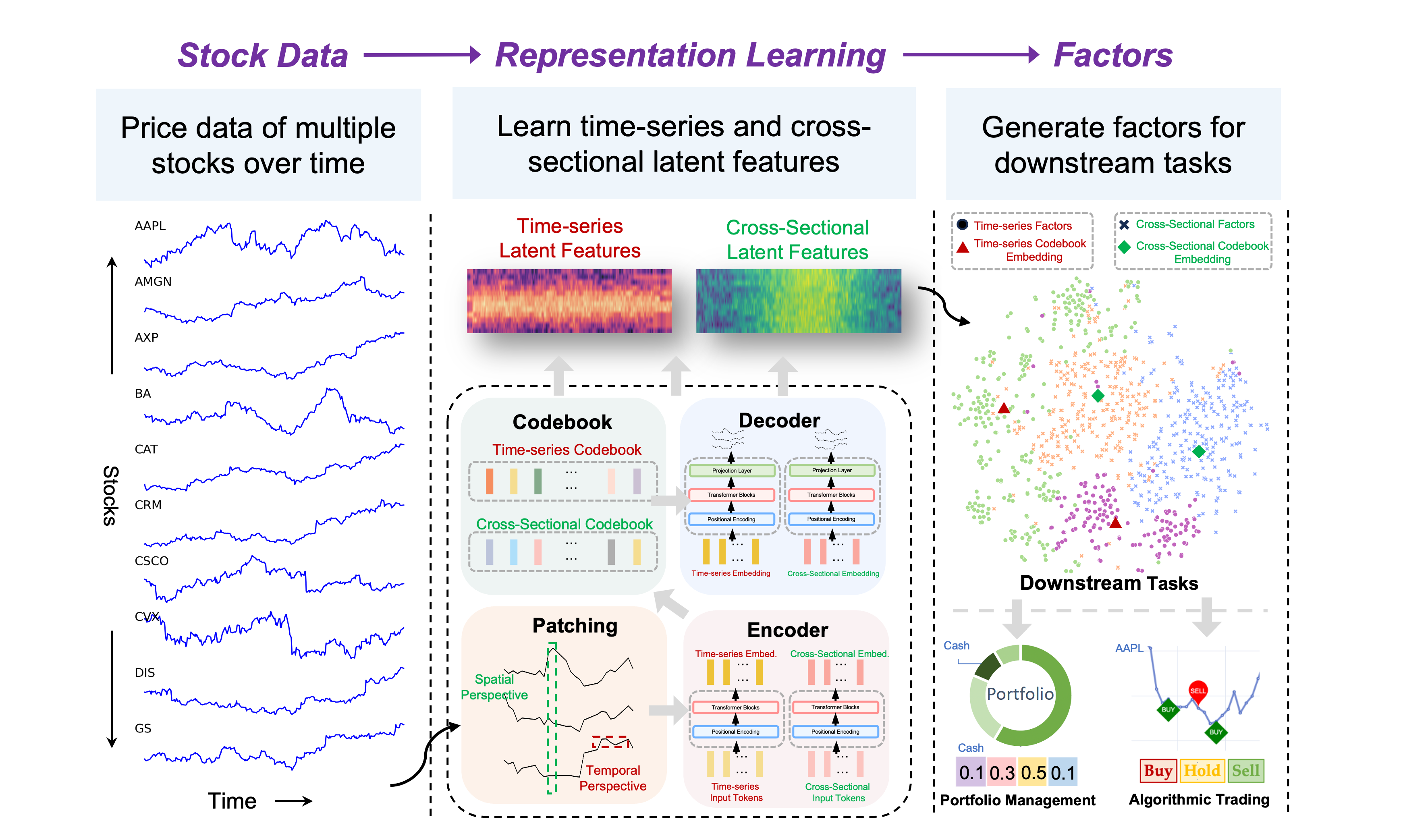
STORM: A Spatio-Temporal Factor Model Based on Dual Vector Quantized Variational Autoencoders for Financial Trading
Yilei Zhao*, Wentao Zhang*, Tingran Yang, Yong Jiang, Fei Huang, Wei Yang Bryan Lim†
Proceedings of the Nineteenth ACM International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining (WSDM), 2026
In financial trading, factor models are widely used to price assets and capture excess returns from mispricing. Recently, we have witnessed the rise of variational autoencoder-based latent factor models, which learn latent factors self-adaptively. While these models focus on modeling overall market conditions, they often fail to effectively capture the temporal patterns of individual stocks. Additionally, representing multiple factors as single values simplifies the model but limits its ability to capture complex relationships and dependencies. As a result, the learned factors are of low quality and lack diversity, reducing their effectiveness and robustness across different trading periods. To address these issues, we propose a Spatio-Temporal factOR Model based on dual vector quantized variational autoencoders, named STORM, which extracts features of stocks from temporal and spatial perspectives, then fuses and aligns these features at the fine-grained and semantic level, and represents the factors as multi-dimensional embeddings. The discrete codebooks cluster similar factor embeddings, ensuring orthogonality and diversity, which helps distinguish between different factors and enables factor selection in financial trading. To show the performance of the proposed factor model, we apply it to two downstream experiments: portfolio management on two stock datasets and individual trading tasks on six specific stocks. The extensive experiments demonstrate STORM's flexibility in adapting to downstream tasks and superior performance over baseline models.
# AI4Finance # spatio-temporal learning # factor models # portfolio management # quantitative trading
STORM: A Spatio-Temporal Factor Model Based on Dual Vector Quantized Variational Autoencoders for Financial Trading
Yilei Zhao*, Wentao Zhang*, Tingran Yang, Yong Jiang, Fei Huang, Wei Yang Bryan Lim†
Proceedings of the Nineteenth ACM International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining (WSDM), 2026
In financial trading, factor models are widely used to price assets and capture excess returns from mispricing. Recently, we have witnessed the rise of variational autoencoder-based latent factor models, which learn latent factors self-adaptively. While these models focus on modeling overall market conditions, they often fail to effectively capture the temporal patterns of individual stocks. Additionally, representing multiple factors as single values simplifies the model but limits its ability to capture complex relationships and dependencies. As a result, the learned factors are of low quality and lack diversity, reducing their effectiveness and robustness across different trading periods. To address these issues, we propose a Spatio-Temporal factOR Model based on dual vector quantized variational autoencoders, named STORM, which extracts features of stocks from temporal and spatial perspectives, then fuses and aligns these features at the fine-grained and semantic level, and represents the factors as multi-dimensional embeddings. The discrete codebooks cluster similar factor embeddings, ensuring orthogonality and diversity, which helps distinguish between different factors and enables factor selection in financial trading. To show the performance of the proposed factor model, we apply it to two downstream experiments: portfolio management on two stock datasets and individual trading tasks on six specific stocks. The extensive experiments demonstrate STORM's flexibility in adapting to downstream tasks and superior performance over baseline models.
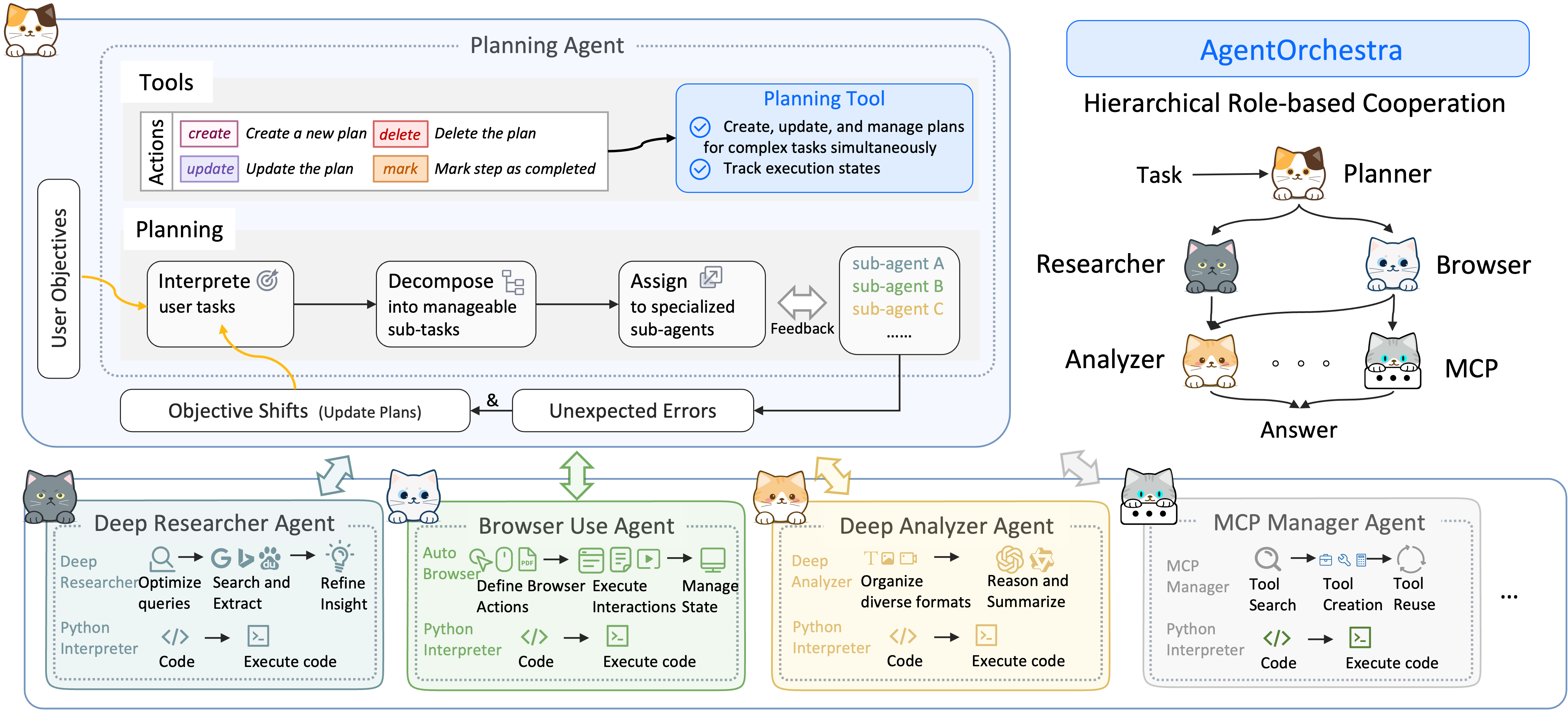
Agentorchestra: A Hierarchical Multi-agent Framework for General-purpose Task Solving
Wentao Zhang, Ce Cui, Yilei Zhao, Rui Hu, Yang Liu, Yahui Zhou, Bo An†
arXiv preprint, 2025
Recent advances in LLMs-based agent systems have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in solving complex tasks. Nevertheless, current protocols (e.g., A2A and MCP) suffer from insufficient capabilities in context management, limited adaptability to diverse environments, and the absence of dynamic agent architectures. To address these limitations, we propose the Tool-Environment-Agent (TEA) Protocol, which establishes a principled basis for integrating environments, agents, and tools into an unified system. The TEA protocol treats environments and agents as first-class resources, enabling comprehensive context management and adaptive environment integration. Based on this protocol, we introduce AgentOrchestra, a hierarchical multi-agent framework with a central planning agent that decomposes complex objectives and coordinates specialized agents. Each sub-agent is dedicated to specific functions, providing capabilities for data analysis, file operations, web navigation, and interactive reasoning. Notably, AgentOrchestra introduces a tool manager agent that supports intelligent evolution through dynamic tool creation, retrieval, and reuse mechanisms. Experiments on three widely used benchmarks show that AgentOrchestra consistently outperforms existing baselines, achieving state-of-the-art performance of 83.39% on GAIA and ranking among the top general-purpose LLM-based agents. These results highlight the effectiveness of the TEA Protocol and hierarchical organization in building general-purpose multi-agent systems.
# LLM Agents # deep research # hierarchical multi-agent systems
Agentorchestra: A Hierarchical Multi-agent Framework for General-purpose Task Solving
Wentao Zhang, Ce Cui, Yilei Zhao, Rui Hu, Yang Liu, Yahui Zhou, Bo An†
arXiv preprint, 2025
Recent advances in LLMs-based agent systems have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in solving complex tasks. Nevertheless, current protocols (e.g., A2A and MCP) suffer from insufficient capabilities in context management, limited adaptability to diverse environments, and the absence of dynamic agent architectures. To address these limitations, we propose the Tool-Environment-Agent (TEA) Protocol, which establishes a principled basis for integrating environments, agents, and tools into an unified system. The TEA protocol treats environments and agents as first-class resources, enabling comprehensive context management and adaptive environment integration. Based on this protocol, we introduce AgentOrchestra, a hierarchical multi-agent framework with a central planning agent that decomposes complex objectives and coordinates specialized agents. Each sub-agent is dedicated to specific functions, providing capabilities for data analysis, file operations, web navigation, and interactive reasoning. Notably, AgentOrchestra introduces a tool manager agent that supports intelligent evolution through dynamic tool creation, retrieval, and reuse mechanisms. Experiments on three widely used benchmarks show that AgentOrchestra consistently outperforms existing baselines, achieving state-of-the-art performance of 83.39% on GAIA and ranking among the top general-purpose LLM-based agents. These results highlight the effectiveness of the TEA Protocol and hierarchical organization in building general-purpose multi-agent systems.
2024
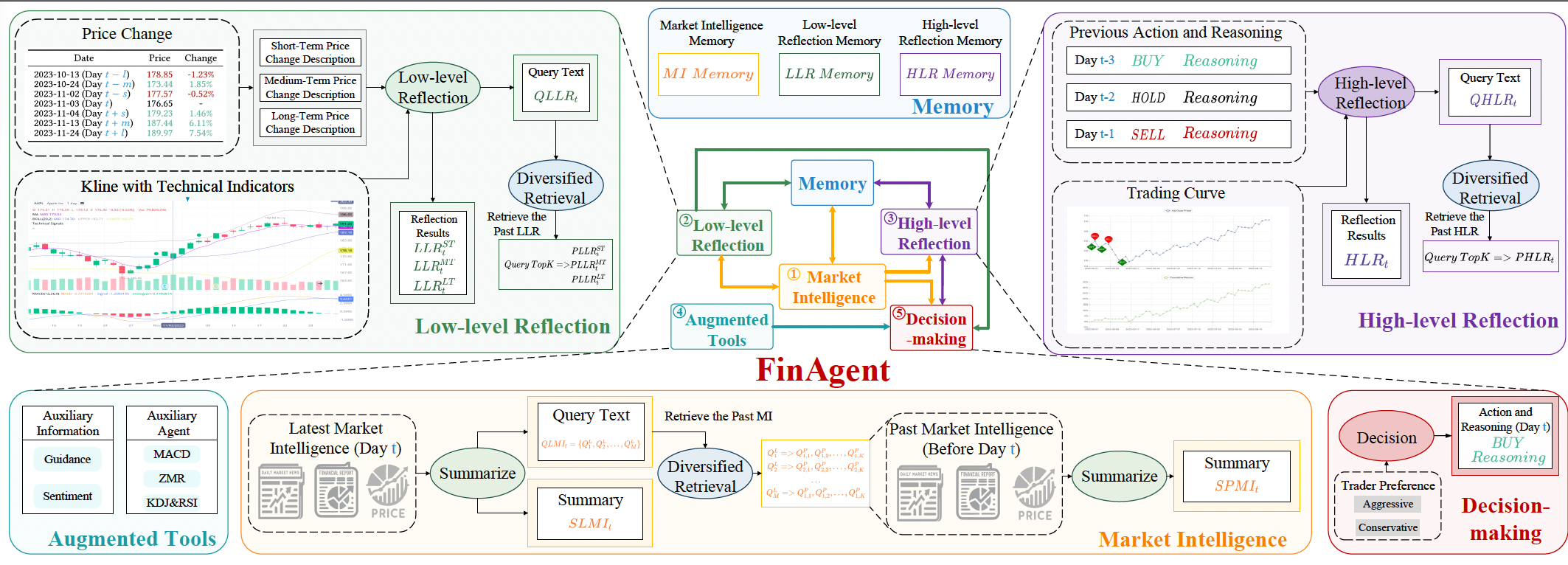
A Multimodal Foundation Agent for Financial Trading: Tool-augmented, Diversified, and Generalist
Wentao Zhang, Lingxuan Zhao, Haochong Xia, Shuo Sun, Jiaze Sun, Molei Qin, Xinyi Li, Yuqing Zhao, Yilei Zhao, Xinyu Cai, Longtao Zheng, Xinrun Wang, Bo An†
Proceedings of the 30th ACM SIGKDD conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Dining (KDD), 2024
Large language model-based explainable recommendation (LLM-based ER) systems can provide remarkable human-like explanations and have widely received attention from researchers. However, the original LLM-based ER systems face three low-quality problems in their generated explanations, i.e., lack of personalization, inconsistency, and questionable explanation data. To address these problems, we propose a novel LLM-based ER model denoted as LLM2ER to serve as a backbone and devise two innovative explainable quality reward models for fine-tuning such a backbone in a reinforcement learning paradigm, ultimately yielding a fine-tuned model denoted as LLM2ER-EQR, which can provide high-quality explanations. LLM2ER-EQR can generate personalized, informative, and consistent high-quality explanations learned from questionable-quality explanation datasets. Extensive experiments conducted on three real-world datasets demonstrate that our model can generate fluent, diverse, informative, and highly personalized explanations.
# AI4Finance # LLM Agents # quantitative trading
A Multimodal Foundation Agent for Financial Trading: Tool-augmented, Diversified, and Generalist
Wentao Zhang, Lingxuan Zhao, Haochong Xia, Shuo Sun, Jiaze Sun, Molei Qin, Xinyi Li, Yuqing Zhao, Yilei Zhao, Xinyu Cai, Longtao Zheng, Xinrun Wang, Bo An†
Proceedings of the 30th ACM SIGKDD conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Dining (KDD), 2024
Large language model-based explainable recommendation (LLM-based ER) systems can provide remarkable human-like explanations and have widely received attention from researchers. However, the original LLM-based ER systems face three low-quality problems in their generated explanations, i.e., lack of personalization, inconsistency, and questionable explanation data. To address these problems, we propose a novel LLM-based ER model denoted as LLM2ER to serve as a backbone and devise two innovative explainable quality reward models for fine-tuning such a backbone in a reinforcement learning paradigm, ultimately yielding a fine-tuned model denoted as LLM2ER-EQR, which can provide high-quality explanations. LLM2ER-EQR can generate personalized, informative, and consistent high-quality explanations learned from questionable-quality explanation datasets. Extensive experiments conducted on three real-world datasets demonstrate that our model can generate fluent, diverse, informative, and highly personalized explanations.
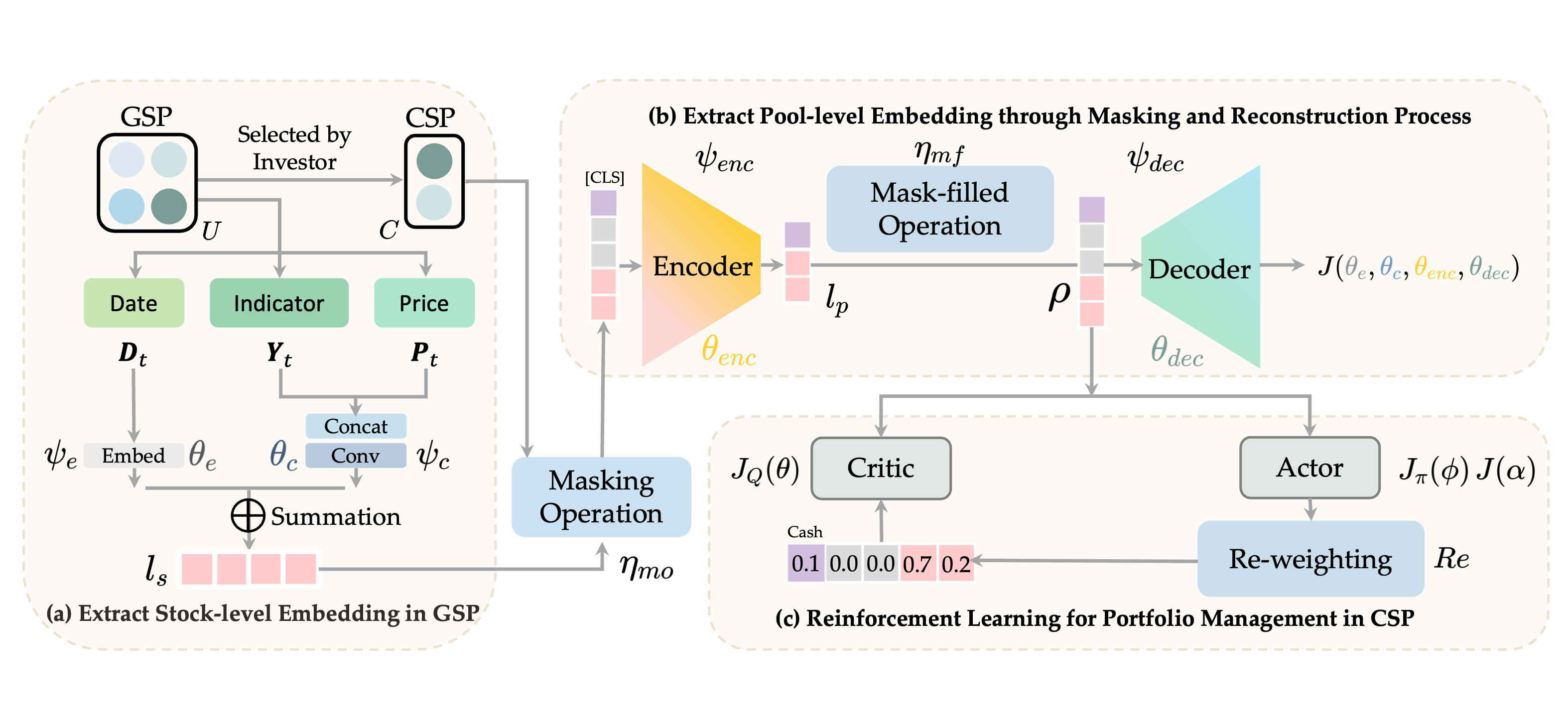
Reinforcement Learning with Maskable Stock Representation for Portfolio Management in Customizable Stock Pools
Wentao Zhang, Yilei Zhao, Shuo Sun, Jie Ying, Yonggang Xie, Zitao Song, Xinrun Wang, Bo An†
Proceedings of the ACM Web Conference (WWW), 2024
Portfolio management (PM) is a fundamental financial trading task, which explores the optimal periodical reallocation of capitals into different stocks to pursue long-term profits. Reinforcement learning (RL) has recently shown its potential to train profitable agents for PM through interacting with financial markets. However, existing work mostly focuses on fixed stock pools, which is inconsistent with investors' practical demand. Specifically, the target stock pool of different investors varies dramatically due to their discrepancy on market states and individual investors may temporally adjust stocks they desire to trade (e.g., adding one popular stocks), which lead to customizable stock pools (CSPs). Existing RL methods require to retrain RL agents even with a tiny change of the stock pool, which leads to high computational cost and unstable performance. To tackle this challenge, we propose EarnMore, a rEinforcement leARNing framework with Maskable stOck REpresentation to handle PM with CSPs through one-shot training in a global stock pool (GSP). Specifically, we first introduce a mechanism to mask out the representation of the stocks outside the target pool. Second, we learn meaningful stock representations through a self-supervised masking and reconstruction process. Third, a re-weighting mechanism is designed to make the portfolio concentrate on favorable stocks and neglect the stocks outside the target pool. Through extensive experiments on 8 subset stock pools of the US stock market, we demonstrate that EarnMore significantly outperforms 14 state-of-the-art baselines in terms of 6 popular financial metrics with over 40% improvement on profit.
# AI4Finance # portfolio management # reinforcement learning
Reinforcement Learning with Maskable Stock Representation for Portfolio Management in Customizable Stock Pools
Wentao Zhang, Yilei Zhao, Shuo Sun, Jie Ying, Yonggang Xie, Zitao Song, Xinrun Wang, Bo An†
Proceedings of the ACM Web Conference (WWW), 2024
Portfolio management (PM) is a fundamental financial trading task, which explores the optimal periodical reallocation of capitals into different stocks to pursue long-term profits. Reinforcement learning (RL) has recently shown its potential to train profitable agents for PM through interacting with financial markets. However, existing work mostly focuses on fixed stock pools, which is inconsistent with investors' practical demand. Specifically, the target stock pool of different investors varies dramatically due to their discrepancy on market states and individual investors may temporally adjust stocks they desire to trade (e.g., adding one popular stocks), which lead to customizable stock pools (CSPs). Existing RL methods require to retrain RL agents even with a tiny change of the stock pool, which leads to high computational cost and unstable performance. To tackle this challenge, we propose EarnMore, a rEinforcement leARNing framework with Maskable stOck REpresentation to handle PM with CSPs through one-shot training in a global stock pool (GSP). Specifically, we first introduce a mechanism to mask out the representation of the stocks outside the target pool. Second, we learn meaningful stock representations through a self-supervised masking and reconstruction process. Third, a re-weighting mechanism is designed to make the portfolio concentrate on favorable stocks and neglect the stocks outside the target pool. Through extensive experiments on 8 subset stock pools of the US stock market, we demonstrate that EarnMore significantly outperforms 14 state-of-the-art baselines in terms of 6 popular financial metrics with over 40% improvement on profit.
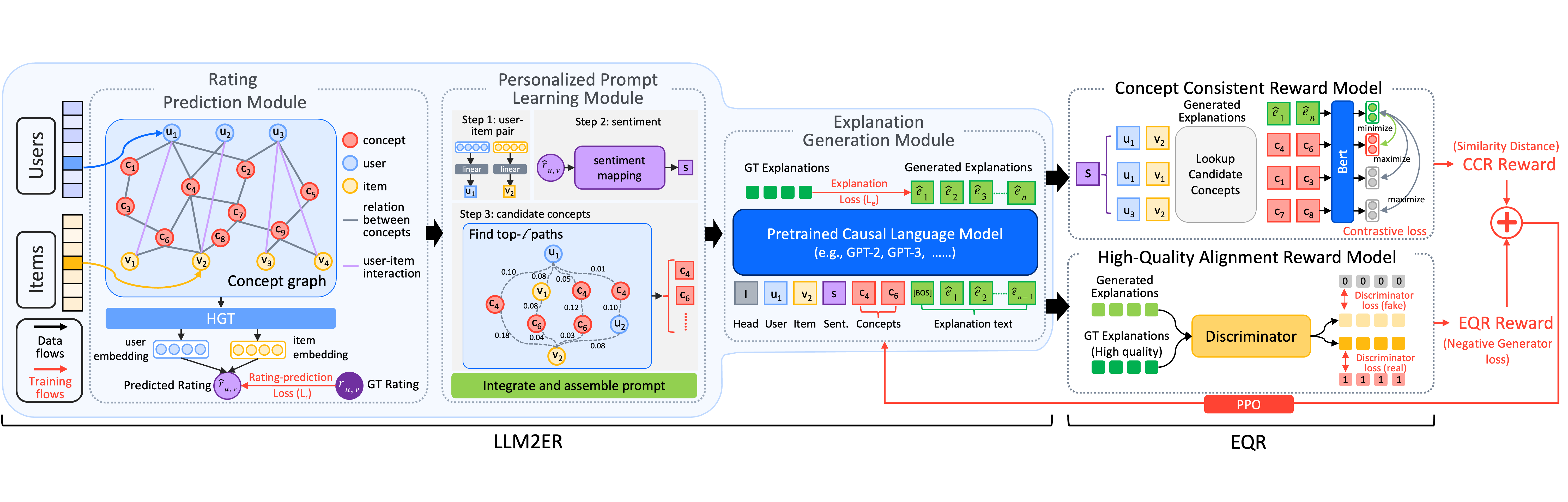
Fine-tuning Large Language Model based Explainable Recommendation with Explainable Quality Reward
Mengyuan Yang, Mengying Zhu†, Yan Wang, Linxun Chen, Yilei Zhao, Xiuyuan Wang, Bing Han, Xiaolin Zheng, Jianwei Yin
Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI), 2024
Large language model-based explainable recommendation (LLM-based ER) systems can provide remarkable human-like explanations and have widely received attention from researchers. However, the original LLM-based ER systems face three low-quality problems in their generated explanations, i.e., lack of personalization, inconsistency, and questionable explanation data. To address these problems, we propose a novel LLM-based ER model denoted as LLM2ER to serve as a backbone and devise two innovative explainable quality reward models for fine-tuning such a backbone in a reinforcement learning paradigm, ultimately yielding a fine-tuned model denoted as LLM2ER-EQR, which can provide high-quality explanations. LLM2ER-EQR can generate personalized, informative, and consistent high-quality explanations learned from questionable-quality explanation datasets. Extensive experiments conducted on three real-world datasets demonstrate that our model can generate fluent, diverse, informative, and highly personalized explanations.
# recommender system # LLM fine-tuning # explainability
Fine-tuning Large Language Model based Explainable Recommendation with Explainable Quality Reward
Mengyuan Yang, Mengying Zhu†, Yan Wang, Linxun Chen, Yilei Zhao, Xiuyuan Wang, Bing Han, Xiaolin Zheng, Jianwei Yin
Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI), 2024
Large language model-based explainable recommendation (LLM-based ER) systems can provide remarkable human-like explanations and have widely received attention from researchers. However, the original LLM-based ER systems face three low-quality problems in their generated explanations, i.e., lack of personalization, inconsistency, and questionable explanation data. To address these problems, we propose a novel LLM-based ER model denoted as LLM2ER to serve as a backbone and devise two innovative explainable quality reward models for fine-tuning such a backbone in a reinforcement learning paradigm, ultimately yielding a fine-tuned model denoted as LLM2ER-EQR, which can provide high-quality explanations. LLM2ER-EQR can generate personalized, informative, and consistent high-quality explanations learned from questionable-quality explanation datasets. Extensive experiments conducted on three real-world datasets demonstrate that our model can generate fluent, diverse, informative, and highly personalized explanations.